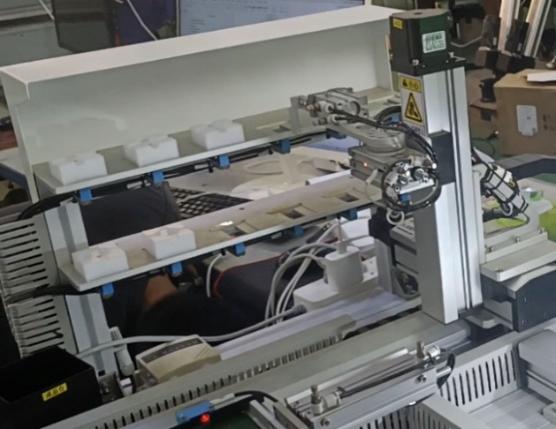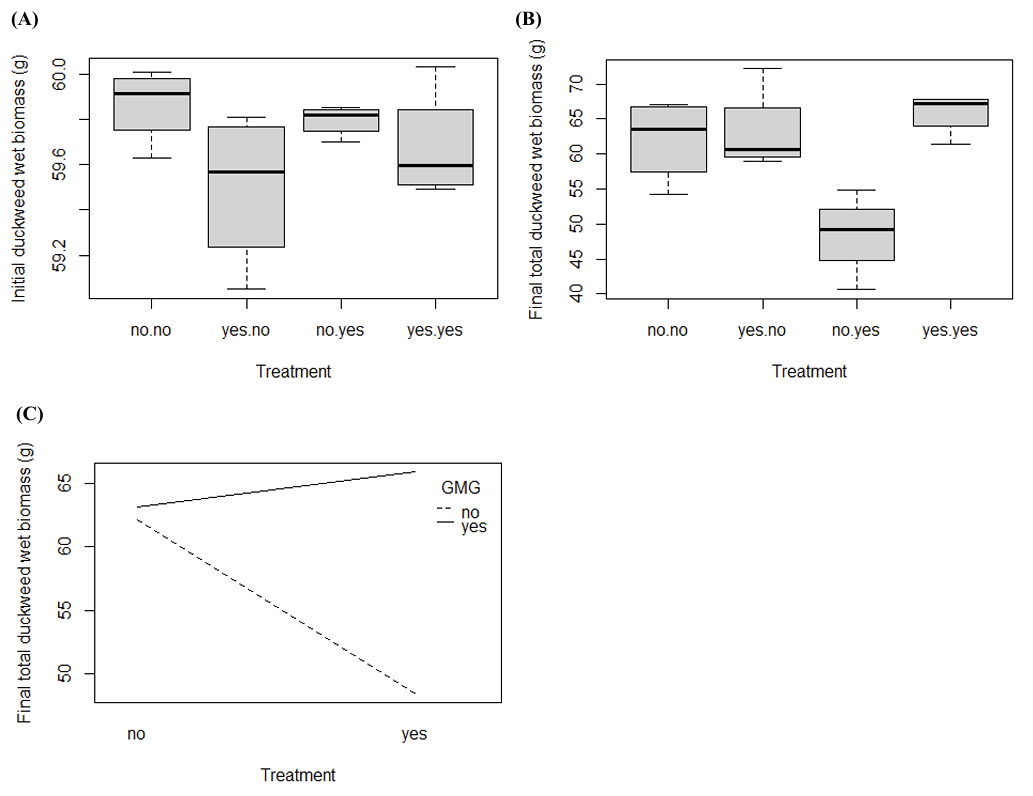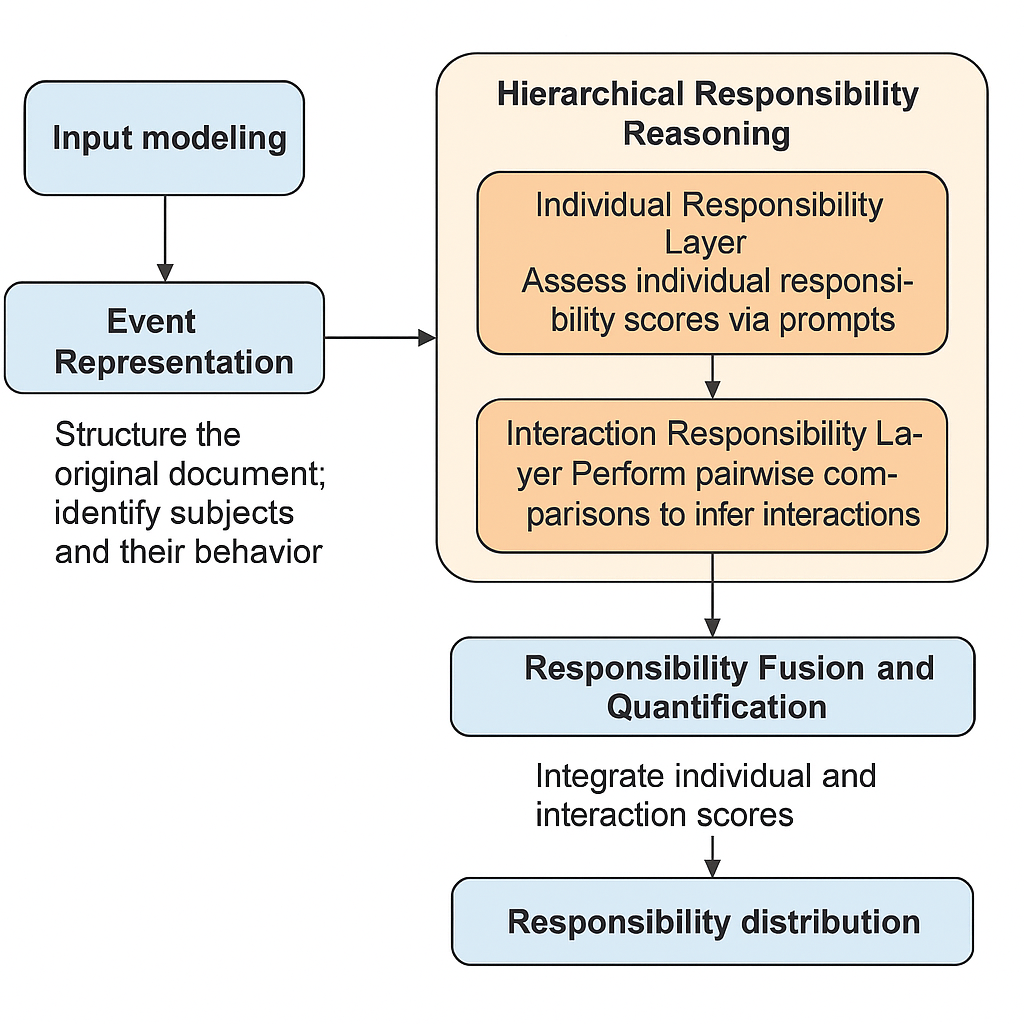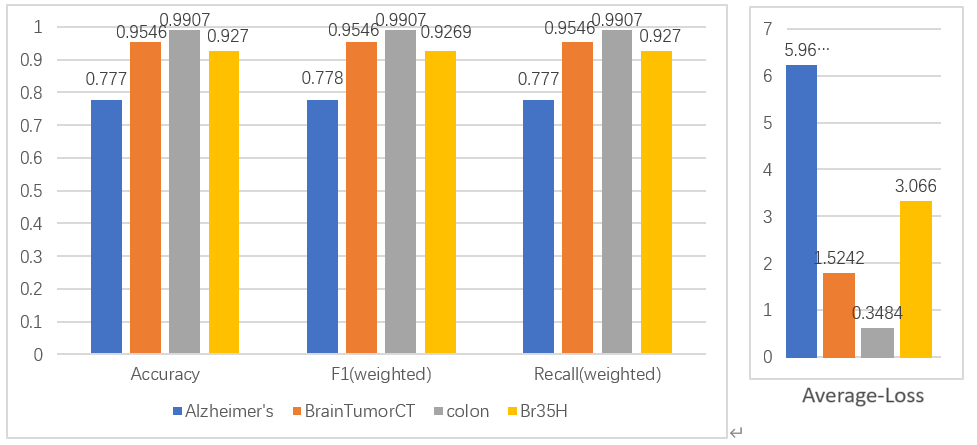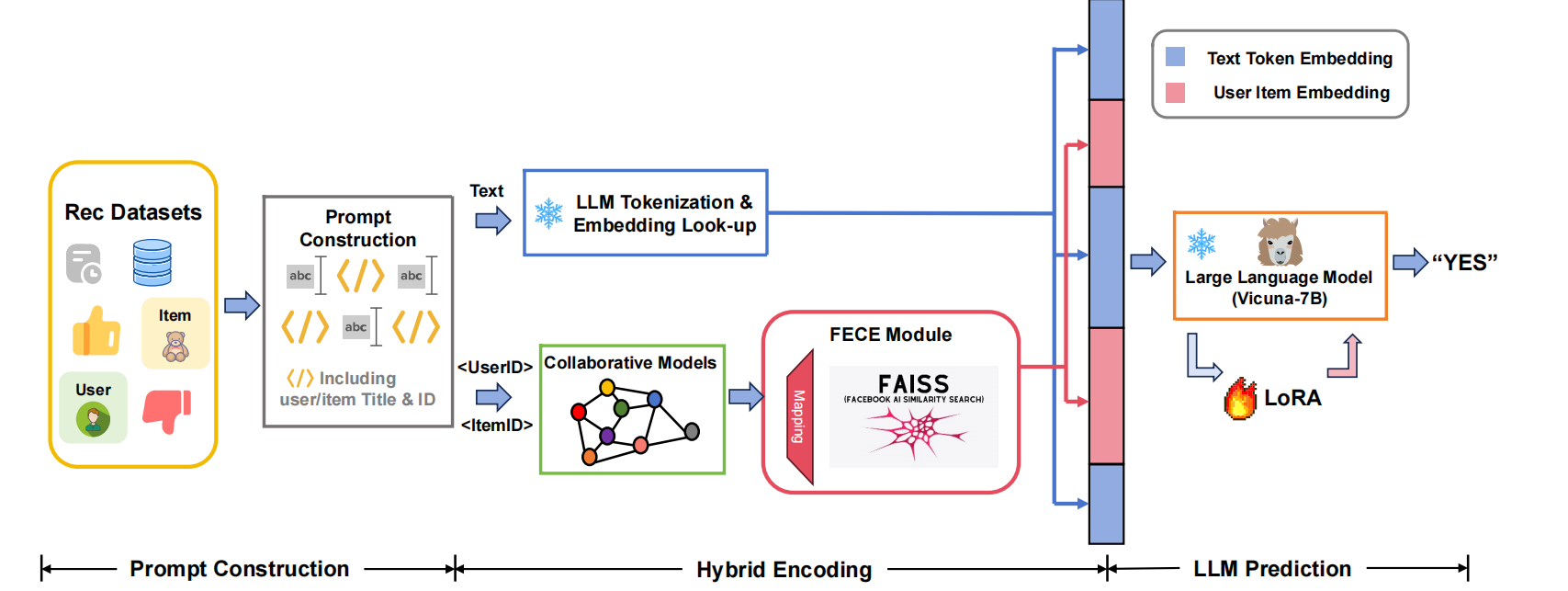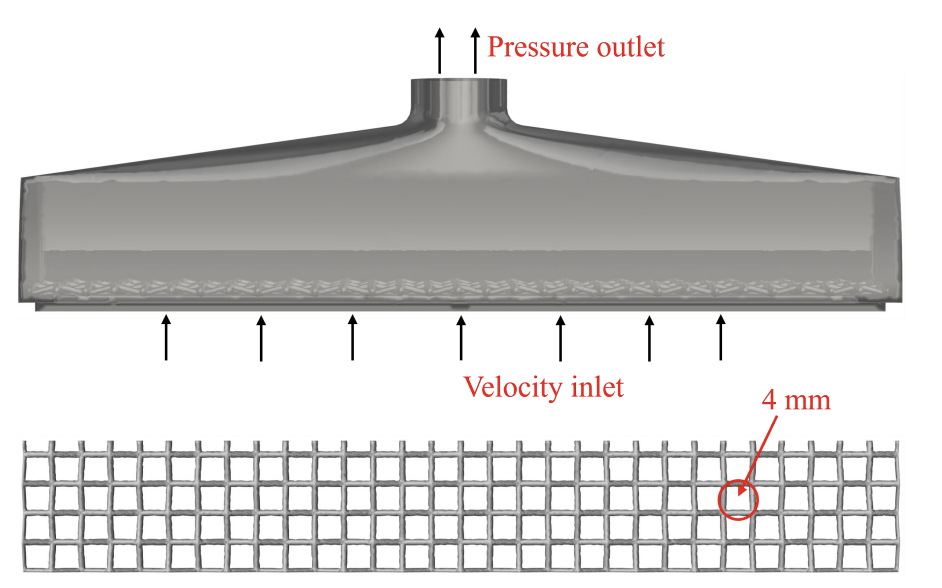
(1) Background: To address the issues of tobacco flue-cured tobacco particles clogging sieve holes during vibration screening, which affects detection accuracy and causes material mixing, (2) Method: The CFD-DEM coupling method was employed to simulate the dynamic behavior of flexible tobacco particles during the cleaning process. By introducing a viscoelastic surface energy contact model, the influence of operational parameters on cleaning efficiency was systematically analyzed. (3) Results: Within the inlet velocity range of 12 m/s to 20 m/s, the optimal flow field structure was achieved at 16 m/s. At a vibration frequency of 50 Hz, the system reached optimal energy transfer efficiency with the most uniform particle velocity distribution. Although high-frequency vibration improves cleaning efficiency, it intensifies particle force fluctuations. (4) Conclusion: This study provides a theoretical basis for the intelligent design of tobacco flue-cured tobacco cleaning devices.