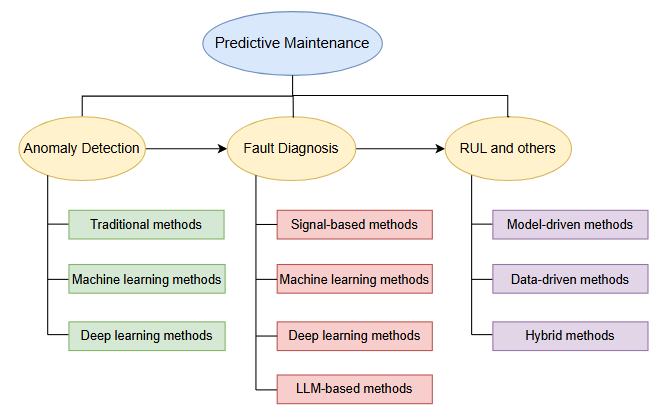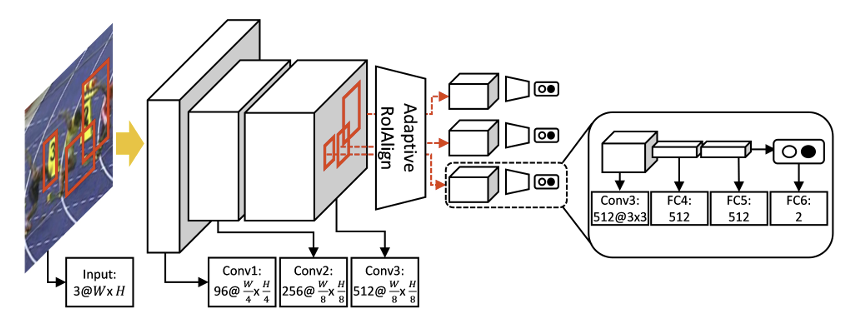
Wall structures are commonly seen in everyday life, with brick masonry and concrete being the most frequently used materials. However, in the face of natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, or other extreme situations, these buildings may collapse, leading to serious casualties and significant property damage. This paper aims to discuss the research and development of new wall materials and explore the compressive strength and seismic performance of modern wall materials in natural disasters. It is found that modern wall materials have witnessed significant improvement in seismic performance, making them especially suitable for meeting lighting needs during nighttime earthquakes. The research and development of self-luminous glass fibre-reinforced plastic (GFRP) composite materials can provide lighting during power outages, enhancing residents' sense of security. In addition, inspired by bioluminescence, specifically the light-emitting mechanism of fireflies, a new type of self-luminous material has been developed through the reaction between luciferin and luciferase. It offers an environmentally friendly and efficient lighting solution during blackouts.