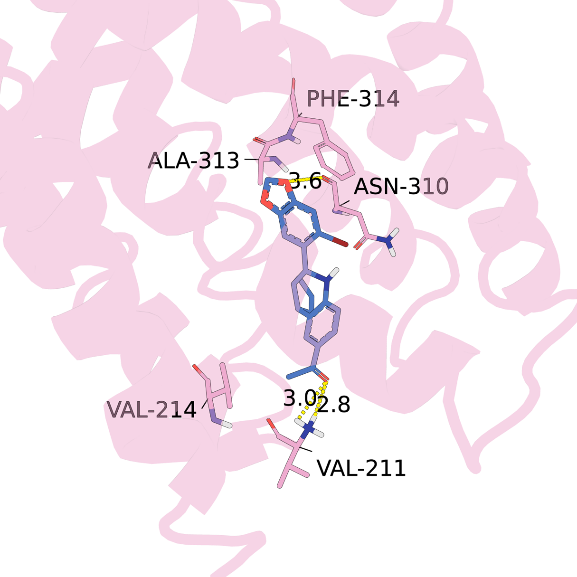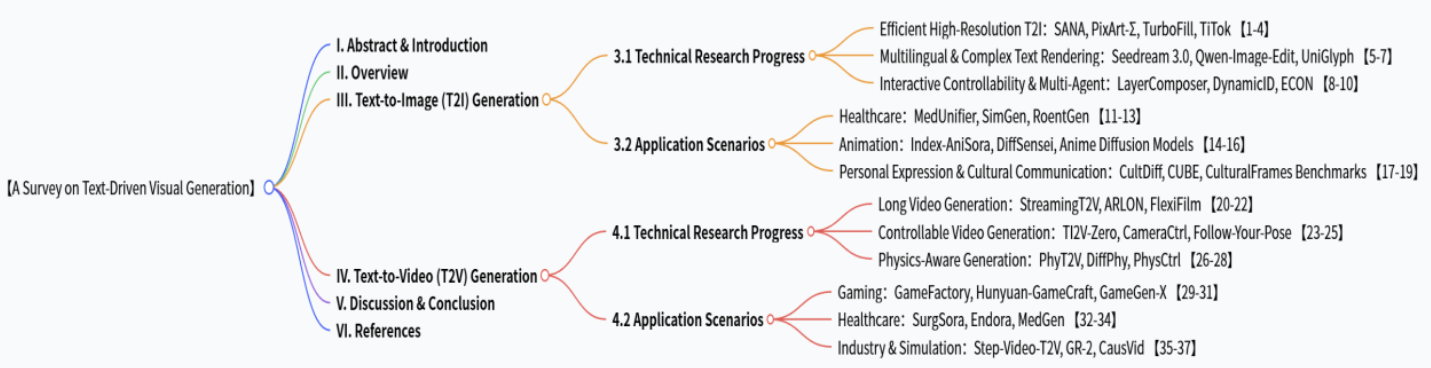
After DDPM outperformed GANs, diffusion models have evolved into the backbone of text-guided visual generation, with Stable Diffusion and DALL·E 2 alleviating key technical constraints. Despite remarkable advances in T2I and T2V tasks, critical gaps remain unaddressed. This paper conducts a systematic review of diffusion-based T2I and T2V technologies, synthesises the latest advances in related technologies, and proposes a “Technical Module-Application-Evaluation” framework to link technical breakthroughs with real-world applications. It also highlights under-researched fields and corresponding evaluation benchmarks, offering an integrated technical landscape to guide the equitable and reliable industrialisation of text-driven visual generation technologies.