About AEIAdvances in Engineering Innovation (AEI) is a peer-reviewed, fast-indexing open access journal hosted by Tianjin University Research Centre on Data Intelligence and Cloud-Edge-Client Service Engineering and published by EWA Publishing. AEI is published monthly, and it is a comprehensive journal focusing on multidisciplinary areas of engineering and at the interface of related subjects, including, but not limited to, Computer Science, Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Mechanical Engineering & Automation, Chemical & Environmental Engineering, Civil Engineering, etc.For the details about the AEI scope, please refer to the Aims and Scope page. For more information about the journal, please refer to the FAQ page or contact info@ewapublishing.org. |
| Aims & scope of AEI are: · Computer Science · Electrical & Electronic Engineering · Mechanical Engineering & Automation · Chemical & Environmental Engineering · Civil Engineering |
Article processing charge
A one-time Article Processing Charge (APC) of 450 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review. excluding taxes.
Open access policy
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. (CC BY 4.0 license).
Your rights
These licenses afford authors copyright while enabling the public to reuse and adapt the content.
Peer-review process
Our blind and multi-reviewer process ensures that all articles are rigorously evaluated based on their intellectual merit and contribution to the field.
Editors View full editorial board

Chicago, USA
momar3@iit.edu

Tianjin, China
rgz@tju.edu.cn

Tianjin, China
zhangli2006@tust.edu.cn

Boston, USA
rkpaul@bu.edu
Latest articles View all articles
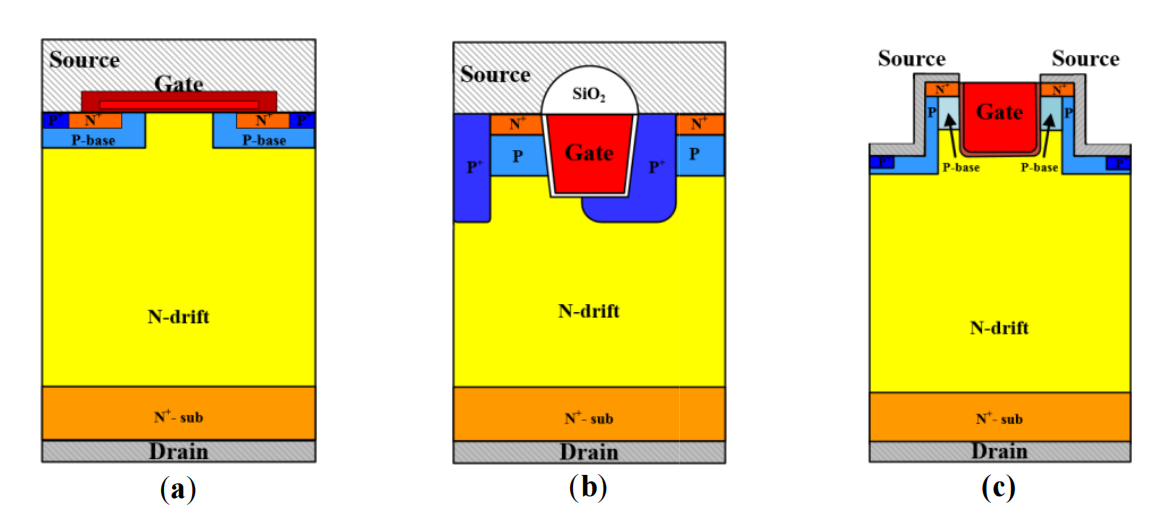
This study investigates the Total Ionizing Dose (TID) effects in commercial 1200 V SiC MOSFET power devices with planar, trench, and double-trench structures. Radiation test results indicate that, with the accumulation of radiation dose, the transfer characteristic curves of all three device structures exhibit a negative shift. However, differences are observed in their breakdown characteristics. The breakdown curve of the planar-structure device shows no degradation with increasing radiation dose, whereas the breakdown characteristic curves of the trench and double-trench structures deteriorate as the radiation dose accumulates.

 View pdf
View pdf



Microplastic pollution in global aquatic ecosystems poses an imminent threat to both ecological integrity and human wellbeing. These minuscule particles (<5 mm), derived from anthropogenic activities, accumulate organic pollutants and heavy metals, permeating the food chain and triggering reproductive abnormalities and endocrine disruption in organisms. Particles with diameters smaller than 100 μm are particularly insidious, owing to their diminutive size, which facilitates greater bioaccumulation while rendering them significantly more challenging to collect and detect. Drawing inspiration from the highly efficient filtration mechanism of sabellid worms, this study proposes the design of an aquatic microplastic adsorption robot that mimics the feather-like radiolar crown structure of these organisms. The robot incorporates a flexible polymeric vibrating membrane system, a solid monolithic magnetic porous polymer material (PDVB-Fe₃O₄), and underwater adsorption suction cups to achieve efficient capture of minute microplastics (diameters less than 100 μm). Post-collection, the adsorption module enables rapid desorption, thereby facilitating facile onshore analysis and detection. The authors adopted computational fluid dynamics (CFD) methods to develop a fluid-solid coupling model, simulating five water environments with varying flow velocities: 0.05 m/s, 0.07 m/s, 0.09 m/s, 0.2 m/s, and 0.5 m/s. The results validated the robotic system's in-water performance, revealing low energy consumption and favorable stability (data). This design offers a scalable technical solution for achieving the Sustainable Development Goal 14 (SDG14) target.

 View pdf
View pdf



In this project, we develop a convolutional neural network (CNN) to classify handwritten digits from the MNIST dataset, a widely used benchmark in computer vision. Unlike traditional image-processing pipelines that rely on engineered features, CNNs automatically learn hierarchical representations directly from raw pixel data. Our model consists of two convolutional layers, max pooling, dropout for regularization, and two fully connected layers. Trained for five epochs using the Adadelta optimizer with learning rate decay, the network achieves a test accuracy of 98.92%. These results demonstrate that even a relatively small CNN can achieve strong performance on MNIST with minimal tuning.

 View pdf
View pdf


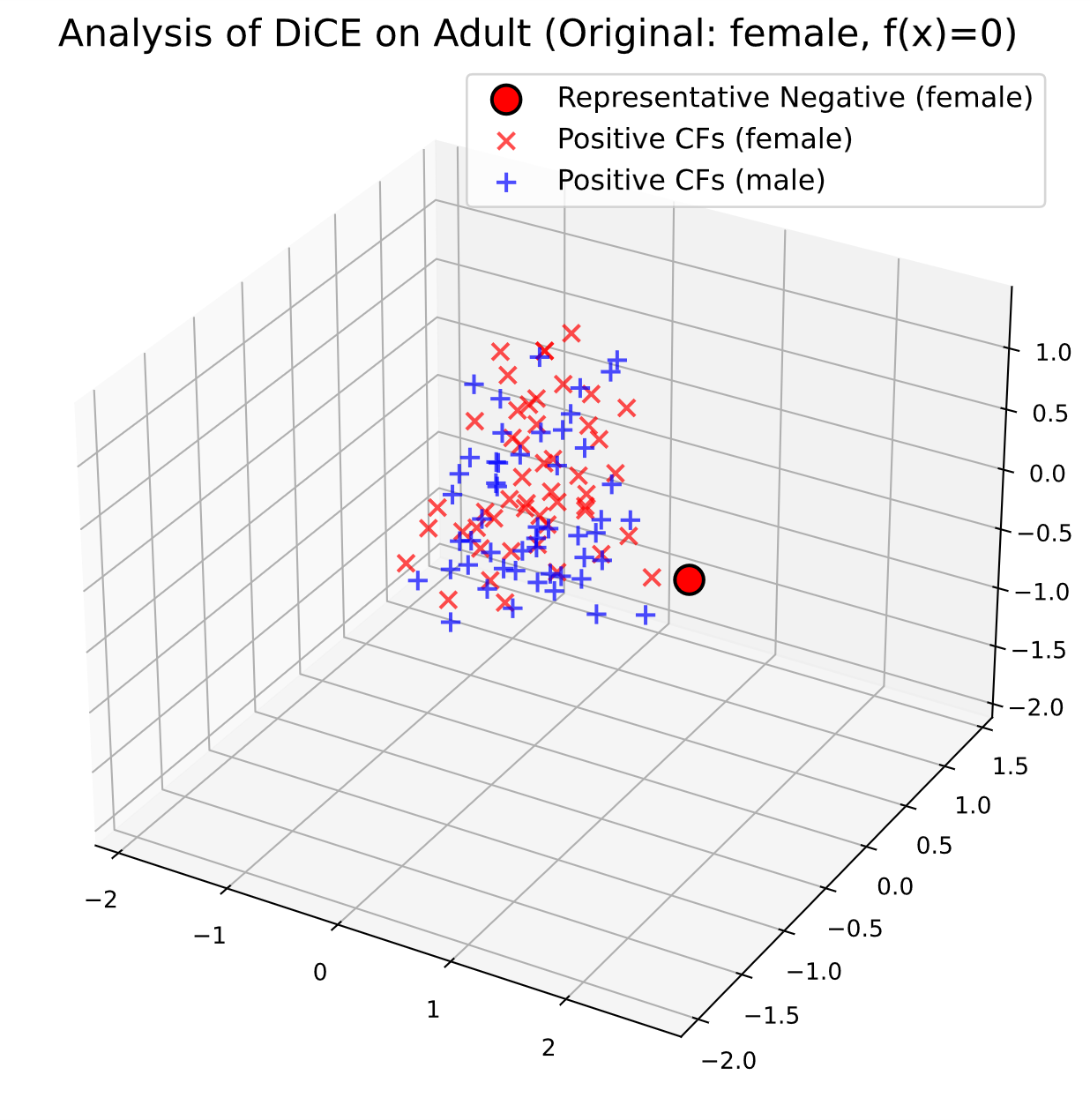
Artificial intelligence regulations typically require that sensitive attributes (such as gender and race) be excluded from algorithmic decision-making to prevent discrimination, a principle commonly referred to as ''fairness through unawareness.'' However, even when sensitive attributes are removed, algorithmic models may still infer such information through proxy variables that are pervasive in data, often via complex nonlinear relationships, thereby perpetuating or even amplifying systemic bias. To address the problem of indirect discrimination under fairness through unawareness, this paper proposes an end-to-end framework that integrates discrimination auditing, diagnosis, and mitigation. First, by incorporating an advanced Transformer-Based Counterfactual Explainer (TABCF), our framework constructs a more reliable bias auditing system capable of accurately uncovering discriminatory behaviors in models. Second, once bias is detected, we introduce an innovative two-stage NOCCO–Shapley diagnostic method that identifies the key proxy variables responsible for discrimination and reveals how the model actually exploits these variables in practice. Finally, to mitigate the identified bias, we implement an adjustable λ-PCF post-processing strategy that enables a quantifiable trade-off between predictive utility and counterfactual fairness without retraining the model. Notably, we find that when the trade-off parameter λ is set to the prior probability distribution of the sensitive attribute in the dataset, the model achieves an optimal balance between fairness and utility. Extensive experiments on four widely used real-world datasets demonstrate that our end-to-end framework not only outperforms existing methods in auditing and diagnosis, but also provides a practical and effective technical pathway for deploying more responsible and fair AI systems in real-world applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumes View all volumes
Announcements View all announcements
Advances in Engineering Innovation
We pledge to our journal community:
We're committed: we put diversity and inclusion at the heart of our activities...
Advances in Engineering Innovation
The statements, opinions and data contained in the journal Advances in Engineering Innovation (AEI) are solely those of the individual authors and contributors...
Indexing
The published articles will be submitted to following databases below:





